 offers you two choices
offers you two choicesAs the name implies, recode means replace some or all codes of a variable by new, different codes.
 offers you two choices
offers you two choices
When in doubt, always create a new variable, as this leaves you with the original untouched, i.e. in case of a mistake (bad recode specifications) you can redo the recode again...
Each form of the command produces a slightly different dialog box:
 Just select the variable or the variables you wish to recode.
Just select the variable or the variables you wish to recode.
 Select the variable or the variables you wish to recode, and for
each of them indicate an Output variable:
give it a name and a label, indicating somehow that it is a derived
variable. When you hit the
button the ? mark in the first field will
be replaced by the name of the new variable to create
Select the variable or the variables you wish to recode, and for
each of them indicate an Output variable:
give it a name and a label, indicating somehow that it is a derived
variable. When you hit the
button the ? mark in the first field will
be replaced by the name of the new variable to create
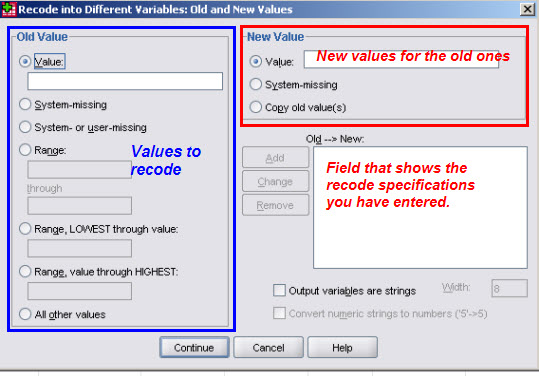 Then click
to
get this dialog
Then click
to
get this dialog
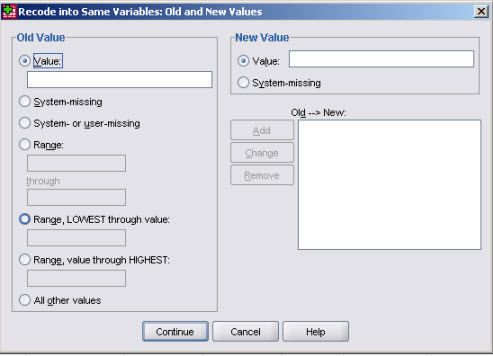 and you will get this dialog if you recode a variable in-place (fewer possibilities
on the Output side.
and you will get this dialog if you recode a variable in-place (fewer possibilities
on the Output side.
A recode is usually a sequence of various recode specifications instructing SPSS to change some old value into a new value. The dialog boxes show also a list of specifications already entered (added) using the button.

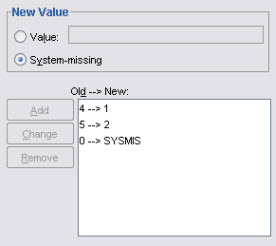
Several recode specifications have already been entered...
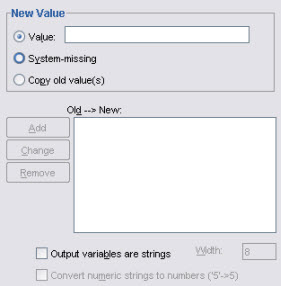 New value section (recode into different variables):
Same specifications as above, plus
New value section (recode into different variables):
Same specifications as above, plus
In addition to these possibilities, lets you transform numeric variables into string variables or string variables into numeric variables. Check the documentation if you need to know more about this.
The first Recode dialog offers also an button that lets you perform a conditional RECODE, i.e. you only recode the cases corresponding to a logical condition. E.g. you could perform a particular recode for women only, but not for men.
Recode specifications list what old values you want to recode into new values; all values not specified will be left untouched, i.e. stay the same as they were before starting the recode, i.e. if you "forget" some values they will simply be left untouched. This is quite obvious with , but also for but with different consequences: if the target variable already exists (SPSS will warn you), only the cases matching the specifications will be changed (overwritten), all others will be left untouched. If the target variable does not exist (new variable), SPSS creates it and sets all values to SYSMIS, therefore if your recoding scheme does not cover all values of the original variable, the corresponding observation in the new variable will stay SYSMIS.
If your Recode creates a new variable, no properties will be defined except the variable label if you indicated it with the target variable name.
In all other situations, RECODE only affects the data values, i.e. value labels and other properties will remain as before, unless you change them explicitly. Assume a simple example of a sex of respondent variable coded 1 for male and 2 for female with appropriate labels. Now recode 1 into 2 and 2 into 1 (reversing the codes)... but the lables will stay as before, i.e. code 1 is still labelled "male", although it now corresponds to women... So please be careful to modify the variable properties immediately... That is for this reason that I recommend to recode into a new variable to avoid this kind of trap. []