Deconvolution
|
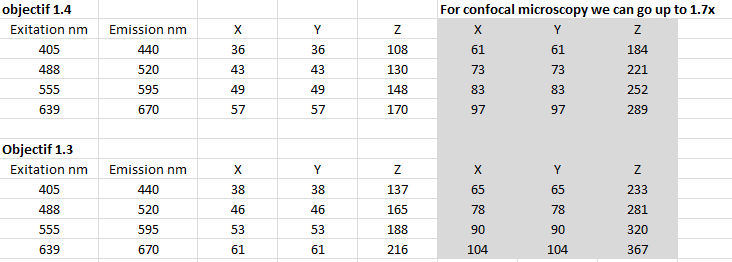
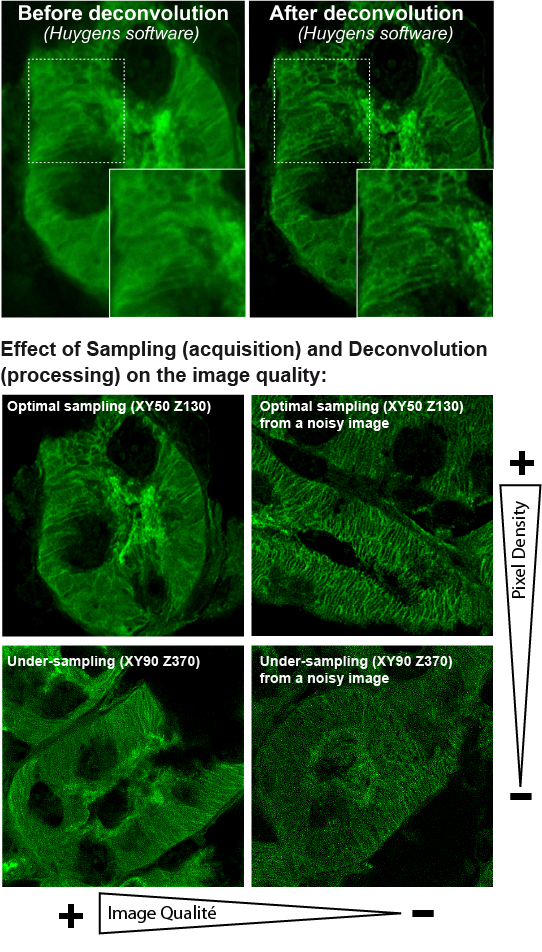
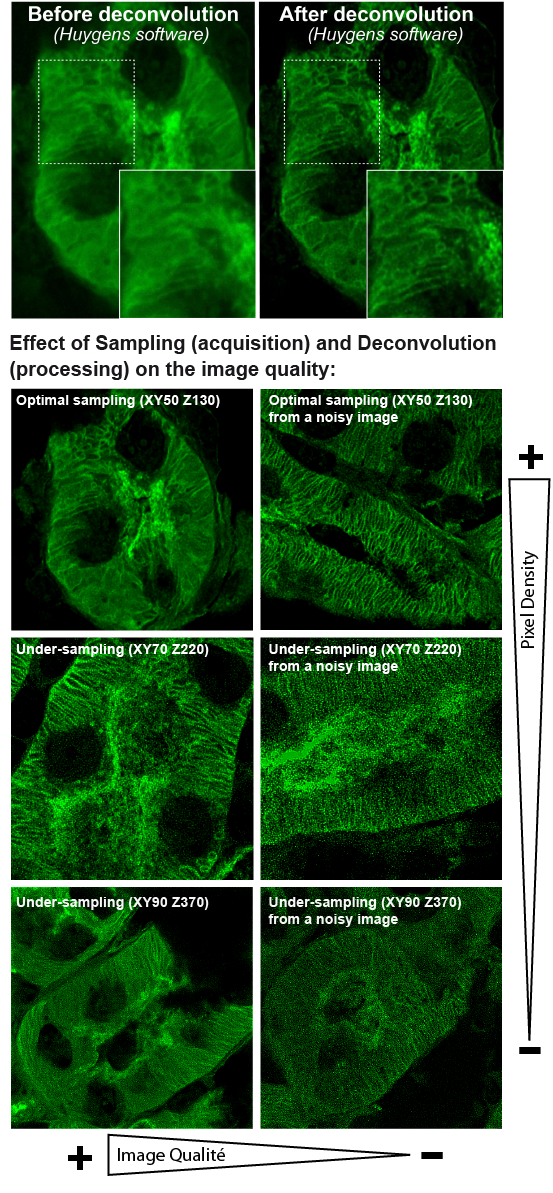
Deconvolution is a mathematical processing method in which computations for the acquired stacks reassign the diffracted light to its original location. Spatial deconvolution can be applied to confocal data, increasing resolution and thus faciliting more profound structural analysis. The quality of deconvolution depends on the quality of the microscopy.
Two types of artefacts must be considered:
Deconvolution is capable of:
|
||
|
|
Recording beads for an experimental PSF.pdf | |
|
|
||
 |