Foreword
The Rectorate of the University of Geneva intends to play a leading role in digital transformation. In order to accompany the University community in this process, it drew up a Digital Strategy in 2018, aiming to develop and enhance the University's expertise in digital technology, to promote the capacity for innovation in terms of teaching, research and digital services, and to develop cooperation with external partners. An Action Plan accompanies this strategy and presents the Rectorate's priority activities and projects for the realization of its strategic objectives. It was developed following various consultations, including workshops on digital technology in November/December 2017 open to the entire university community and external partners, presentations to the deans, a presentation to the University Assembly, interviews with researchers and heads of departments or divisions.
The Action Plan is regularly updated to report on progress and incorporate new digital initiatives or projects that have emerged within the University community. This version includes several projects that have been initiated since the Action Plan was first published or that have taken on new dimensions in the context of the COVID crisis. Projects that have been successfully completed are no longer included, for example the creation of chairs in digital humanities and machine learning, the setting up of a digital innovation cluster (PIN), and the creation of the Office of Digital Transformation. Finally, other projects have been put on hold until circumstances are more favorable, or transformed in order to be integrated into other more advanced projects.
The Digital Strategy Action Plan does not claim to be exhaustive and offers only a partial picture of what is being done in terms of digital transformation at the University. For example, many of the activities of the Division of Information and Communication Systems and Technologies (DiSTIC) are not mentioned in the Action Plan. Similarly, many digital projects carried out by the academic community and central services are not mentioned, even though they contribute to the academic influence of the institution. This Action Plan is therefore a guiding document indicating the activities and projects that the Rectorate particularly wishes to support for the period 2019–2023.
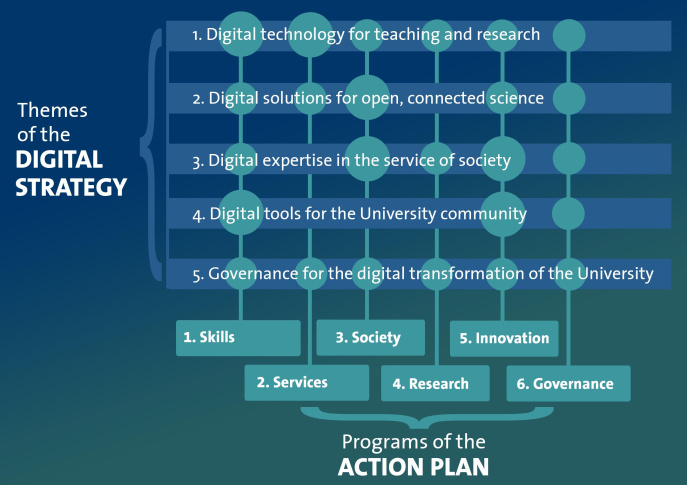
The activities and projects of the Action Plan have been organized into six programs to facilitate steering and monitoring. Each of these programs contributes, to varying degrees, to the different axes of the Digital Strategy, as illustrated in the diagram below.
1. Digital skills for all
The University of Geneva wishes to develop the digital skills of its entire community so that everyone can benefit from digital technology on a daily basis by mastering the essential tools and becoming aware of the challenges related to digital transformation. To achieve this, the institution intends to implement a series of measures that respond to the targeted needs of the various bodies within the institution – students, researchers and administrative staff – and other more general measures open to the entire academic community.
Activities and projects
1.1 Open academic positions dedicated to digital transformation in all faculties
Digital technology offers powerful tools for research and teaching in both the hard sciences and the social sciences and humanities. It also transforms the disciplines taught in the various faculties, both in terms of methodology and content. These developments make it necessary to create new professorships dedicated to the various facets of the digital transformation. These positions will contribute to the development of new fields of research and teaching within the University and should be reference points in the field of digital technology for researchers who wish to integrate digital technology into their work. Within the framework of the COB4, the Rectorate has therefore decided to support the creation of several chairs on digital technology. Positions for an assistant professor in data science and artificial intelligence at the Faculty of Medicine, and an associate professor in digital law at the Faculty of Law, were respectively put out to tender in summer and autumn 2020 thanks to funding from the Convention d'objectifs (COB). Depending on the means available, other positions dedicated to digital technology could be created in the coming years
1.2 Create a digital skills repository (new)
In a world where digital tools are becoming increasingly important, members of the academic community must have a wide range of skills to use these tools and to understand the issues at stake. In this context, it is necessary to create a repository of digital skills for the various populations of the University of Geneva. The creation of such a repository makes it possible to establish a common vocabulary for formulating digital skills policies, and to plan specific training aimed at acquiring the digital skills considered necessary for studying, teaching, conducting research and delivering services.
1.3 Implement an online platform for self-evaluation and self-learning of digital skills
Understanding digital technology requires both a certain general knowledge and training for use of other software or tools. As part of the swissuniversities “Strengthening Digital Skills in Teaching” program, the University of Geneva plans to develop a web platform for students, teaching staff, researchers and members of the administration to test their digital skills and fill any gaps thanks to a personalized visualization tool of their digital skills and a system of training recommendations.
1.4 Create a cross-cutting course on digital transformation
Since September 2020, the University of Geneva has been offering students from all faculties a cross-disciplinary course on digital technology that encompasses the technical, social, ethical, cultural, economic and legal aspects of digital technologies. This optional course is based on all the disciplines taught in the faculties and interfaculty centers. It aims to provide students with a deep awareness of how digital technology is changing society and the means to think and act critically about these changes.
Ultimately, this cross-disciplinary course will become part of a range of courses designed to develop the soft skills of students from all faculties. The cross-disciplinary course on digital technology is offered to students at the end of their bachelor’s and master’s degrees, and leads to ECTS credits. The course takes place over two semesters: the first semester is planned as a general education course, and the second semester is practical workshops on a case study, in which students work in working groups with the aim of developing concrete solutions.
1.5 Train young researchers in digital technologies and related issues
The University wishes to train young researchers in the various aspects of digitalization for their research. As part of the swissuniversity program “Strengthening Digital Skills in Teaching”, the Faculty of Science’s Department of Computer Science has been offering “best practices in computer science” workshops for young researchers since 2019. The Graduate Campus recently set up by the Rectorate has also been able to use swissuniversity resources to offer doctoral students from the institution training modules on various aspects related to digital technology, such as data security, ethical issues, big data and social networks.
1.6 Collaborate with other universities to broaden the online course catalog
Within the framework of the LERU, the University of Geneva participates in the “Virtual exchange for LERU students” project, which gives students enrolled in a partner institution the possibility of obtaining credits by taking online courses, including MOOCs, offered by other universities. A memorandum of understanding has been signed with the universities of the Sorbonne, Leiden, Amsterdam, Utrecht and Munich, and four online distance learning courses are currently being prepared at UNIGE. These courses will be integrated into existing study plans and students taking them will receive ECTS credits after passing an exam in person. By joining this pilot project, the University of Geneva intends to broaden the choice of elective courses offered to students, facilitate student mobility, develop students’ intercultural and digital skills and enable them to familiarize themselves with a training method that will keep them up to date during their future careers.
1.7 Developing e-Learning experience (new)
Digital technology is increasingly being used in education, whether through the use of digital tools or the development of hybrid or even completely distance learning strategies. The use of digital technology in education must be a tool to improve learning and is not an end in itself. Distance learning is a powerful tool for a more inclusive and open university, for example, giving access to educational resources to students who cannot physically follow a traditional classroom-based course. In view of the University’s 2022 accreditation, a reflection has been initiated on the quality of distance education and, more generally, on the use of digital technology in teaching. This reflection has been fed by numerous initiatives taken in the faculties and centers and by the expertise present in various bodies of the institution (TECFA, e-learning cluster, SEA cluster, Center for Continuing and Distance Education, MOOCs unit) and, more recently, by the COVID-19 health crisis, which saw all teaching switched to distance learning within just a few days. These reflections and experiences show that the digital development of teaching is not an easy task. On the strength of this observation, the University intends to work with the faculties and centers to develop technical teaching expertise that can be relied on by teaching staff across the university. In order to facilitate this cooperation and to offer tools and resources to teaching staff, information and support for distance learning have recently been collected and grouped together on a single website. The equipment in the auditoriums and classrooms has also been supplemented in order to facilitate the use of digital tools in teaching.
2. Digital services and support to transform the University
The University wishes to enrich the range of digital services available to the University community so it can take full advantage of the potential offered by digital technology. Whether it be technological improvements, the simplification of certain administrative processes, new services for the web and social networks or the creation of regulations for teleworking, the Rectorate intends to implement a series of measures designed to facilitate work and thus contribute to the performance of the institution.
Activities and projects
2.1 Ensure a seamless online experience for students
Currently, students benefit from a wide range of digital tools that allow them to register at the University, consult their schedules or register for exams. For the most part, these tools have been developed one after the other and their interdependence could be improved. The institution has begun the process of overhauling these IT services with the objective of considerably simplifying and enriching the student experience (SI-student). Ultimately, students will connect to a unified and consistent service from which they can access various important information and initiate administrative procedures. The redesign will also benefit various administrative services and University faculties, which will be able to more simply manage admissions, course and exam scheduling, and the communication of grades to students. It is also an important opportunity for offering new services to users and for coordinating this project with the tools and other media used by students, such as the UNIGE mobile app. The consolidation of online teaching platforms, the real-time delivery of courses, and the generalization of online exams are also concerned.
2.2 Expand the services offered by the University mobile app
The University has created a free mobile app that already offers several practical features for the daily life of students. For example, everyone can use their cellphone to access the rate of attendance of the libraries or to consult the schedules of conferences given in the various buildings.
With the aim of progressively improving the mobile app, the team in charge of its development is working to add new features. The next step is to implement the various course syllabi in the application in autumn 2020, allowing all students to easily organize their schedules. Other functionalities are currently being developed, such as a course schedule, a directory of room plans for university buildings, and a geolocation tool for the library collections, developed jointly with the Scientific Information Division.
2.3 Establish teleworking
As of 1 October 2019, the Rectorate, recognizing teleworking as a driver of productivity and motivation, launched a pilot phase involving about a hundred administrative and technical staff. During the COVID-19 health crisis, the Rectorate gave priority to teleworking for all of its employees whose tasks allow it, extending the scope of this project beyond all expectations. On the basis of the lessons that can be drawn from the pilot phase and the COVID-19 period, the modalities for extending teleworking to all administrative and technical staff, under normal conditions, are being developed and training is being offered to managers.
2.4 Accelerate the digitalization of administrative processes
In order to complete the dematerialization of certain internal processes within the University, and with the aim of facilitating the daily life of users, it is necessary to accelerate the dematerialization of administrative processes. The electronic signature is at the heart of this process, as it simplifies the lifecycle of documents while ensuring their legal value.
Other promising technologies, such as blockchain, could also be tested and analyzed for providing electronic certification services, for example for diplomas. The Rectorate will also make proposals for other processes for which dematerialization is desirable, such as the management of employees’ reimbursement claims, the management of scholarships and student housing rentals, the management of the institution’s IT assets and the management of scientific laboratory consumables.
2.5 Reinforce cybersecurity measures for the University
With the rapid increase in digitalization, the use of cloud services and the risk of attacks on IT systems, strengthening cybersecurity is an institutional priority. This involves not only developing the skills of users and strengthening the fundamentals of IT security, which is always essential (evolution of IT network architecture to make it more secure, security packages for workstations), but also offering advanced functionalities to protect academic and administrative data (encryption and traceability of access, anonymization) and a new paradigm for managing the security of cloud services.
2.6 Define an institutional policy for information governance for the University
Information has become a strategic issue for institutions such as the University of Geneva, whose 6,000 or so employees produce, manage and store large and growing quantities of data and administrative documents, in both paper and digital format. Without taking into account the natively digital traces of this information, the risk of dilution of the institutional memory increases. In order to ensure responsible, secure and sustainable management of information and documents over the medium and long term, it is necessary to put in place a global information governance policy based on document management guidelines and tools. This policy will be based on collaboration with the different entities of the University, thus ensuring the dissemination of an information culture within the institution in the medium and long term.
2.7 Build a platform for University digital publishing in open access
Through the Rectors’ Conference of Swiss Universities, the University of Geneva is co-signatory of the “Berlin Declaration on Open Access to Scientific Knowledge”, making open access publishing one of its strategic objectives. In 2008, the Rectorate adopted a directive on this subject which led to the creation of the UNIGE Open Archive. In 2018, the University launched a pilot project to provide the university community with an online publishing platform for open access journals (Open Journal System). The goal is to provide a hosting solution and management of the publishing process for open access journals edited by UNIGE researchers. Several journals are participating in the pilot phase, the conditions for continuation of which will be examined by the Rectorate by the end of 2020.
2.8 Unify the University presence on social networks
The University firmly believes that social networks are necessary to ensure the visibility of its activities. They are easily accessible and make it possible to communicate clear, concise content enhanced by photos, videos or links to web pages. Videos in particular are nowadays an essential tool for communication for the student body as well as for researchers promoting their work.
In order to guarantee the creation and diffusion of consistent, quality content, ensuring the visibility of the University, an institutional video policy is currently being developed. From September 2020, graphic standards that can be adapted for all faculties, and a new audio identity for videos, answerphones and certain podcasts will be made available to the University community.
2.9 Establish a website support unit
Currently, updates of the unige.ch website are carried out via software that facilitates the editing and publication of web pages. This process allows the webmasters of the departments and faculties to make modifications without having advanced skills in web languages and to quickly provide autonomy to people who wish to manage websites. However, the limits of this method are quickly reached since the possibilities of graphical and technical customization are greatly reduced.
In order to allow the university community to benefit from greater potential in terms of website development, UNIGE plans to create a website support unit, which will have the objective of responding to requests for the creation of websites for events or structures with a strong communication component and going beyond the strict framework of the standard web pages of the UNIGE site. This centralization of web expertise will also allow to keep a graphic coherence of the UNIGE websites.
2.10 Think about the tools and services needed to organize and hold virtual and hybrid events (new)
Digital tools offer new possibilities for rethinking the form and thus the scope of many events organized within the University. As places for meetings and exchanges between experts, for the transmission of knowledge and information to the University community, as well as permanent showcases of the institution’s activities to the outside world, UNIGE events are all living pillars essential to the pursuit of research, teaching and service to the community missions of the University. A reflection on the transformation of these events into virtual or hybrid formats is strategic at multiple levels. The possibility of switching part of the events to virtual or hybrid formats offers new avenues for facilitating the realization of the activities carried out by our ever-growing university community. At a more global level, in addition to enabling greater resilience in sometimes uncertain health contexts, the virtualization of events, particularly scientific events, has the potential to reduce the environmental impact of the international mobility of researchers. Finally, access to these events is facilitated logistically and financially, meaning the regional, national and international influence of UNIGE’s activities is broadened. With a view to accompanying this reflection, the Rectorate has set up an inter-service group whose mission is to propose a vision of the future of events at the UNIGE, accompanied by institutional recommendations (service providers, tools, support).
3. Towards a responsible digital society
The University and the community that it represents are a part of broader society. The University provides services to society through research, innovation and training. Faced with the growing influence of digital technology in people’s daily lives, and for running businesses and administrations, the University aims to develop its digital expertise to serve the Geneva region by making its training more widely accessible and sharing its expertise in digital matters.
Activities and projects
3.1 Identify the impacts of artificial intelligence
Given the importance of current developments in the field of artificial intelligence, it is important to think carefully about the impact that the latter may have on the University’s missions and, more broadly, on society. Some projections show radical changes in certain professions, for example in law, in medicine or in translation and interpretation. There are also ethical, legal and security issues related to the delegation of tasks to machines.
As a result, the University of Geneva intends to create a space for interdisciplinary discussions on the governance issues raised by artificial intelligence, led by the Digital Law Center. This space should allow the exchange of ideas and projects between members of the academic community and with partners from Geneva and international organizations.
3.2 Create a competence center for digital law
The digital world raises many legal questions that affect many areas of law in Switzerland and internationally. These questions particularly concern the legal status of data and data protection, especially personal data. More generally, they cover all the legal issues raised by digital technological developments, in particular artificial intelligence.
The University of Geneva has progressively developed various training and research activities in the field of digital law. A Digital Law Centre is currently being developed in order to pursue and structure these activities and to strengthen the position of the University of Geneva as a center of expertise in this field. The aim is to further raise the University’s profile on these topics nationally and internationally, capitalizing on Geneva’s and Switzerland’s positioning as a place for debate and regulation of digital technology and internet governance at the global level. In particular, the competence center will take advantage of Geneva’s very privileged ecosystem in terms of law and digital governance, which has developed thanks to the activities of numerous international and non-governmental organizations on these themes.
3.3 Provide a certificate of open studies for humanitarian and development contexts
The Rectorate has created a new certificate of complementary training, the certificate of open studies, to respond to the needs of isolated or exiled people or refugees who, thanks to digital technology, can access university level training in their countries, on the roads of exile and in refugee camps. This new certificate responds to the development of innovative teaching formats in a humanitarian context, delivered at a distance in underserved regions or in refugee camps, in response to very specific training needs.
3.4 Discussing digital transformation
The University has significant expertise in digital technology, both in faculties or inter-faculty centers and in administrative services. Likewise, the Geneva ecosystem is home to a multitude of players who are in touch with digital issues: companies, political representatives, members of administrations, teaching staff, international organizations, associations, etc. The University intends to promote meetings between these audiences around current digital issues in the form of regular conferences. These conferences, open to all, aim to discuss the challenges of digital technology with the university community and the community. Given by experts, they deal with topics related to digital in an accessible way and are followed by open discussions. The first conferences are taking place in autumn 2020 in the form of a cycle of four “Let's Talk Digital” conferences. They complement and enrich the transversal course “Understanding Digital Technologies”.
3.5 Initiate reflections and actions for a digital transformation integrating the objectives of sustainable development (new)
The digital transformation brings a multitude of opportunities for our societies, but it is also accompanied by many environmental, social, economic and ethical challenges, as evidenced by the prominent place of digital technology in the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). In order to fully benefit from the potential of the digital transformation and to master its challenges, digital innovation must be at the service of sustainable development. Aware of these challenges, the University of Geneva has placed the digital transformation at the same strategic level as its adherence to the objectives of sustainable development. A reflection group bringing together the Digital Transformation Office (DTO) and the SDG's office has recently been set up with the mission of strengthening collaborative synergies in projects with a digital component. For the time being, two lines of reflection have been defined. On the one hand, a strong will to promote interdisciplinary research combining sustainable development and digital technology, through conferences and joint events. On the other hand, it is planned to reflect on concrete initiatives aimed at promoting good practices in the use of digital technology within the University in partnership with the network of ambassadors of sustainable development.
4. A digital backbone for advanced research
Digital solutions for research are based on information services. These services require state-of-the-art infrastructures whose capabilities are evolving on a daily basis, software that can optimize processes, but also ongoing reflections on how to pool expensive equipment and rare expertise. These facilities are intended to serve researchers through, for example, the deployment of new algorithms, the use of specialized software or the hosting of research data. The University aims to meet institutional needs for computing power and data storage thanks to the development of IT infrastructure and the support of researchers in the use of these facilities through the development of general guidelines, practical tools and expert support.
Activities and projects
4.1 Develop digital infrastructure and services for research
The University wants to increase the capacity of the current IT infrastructure available to researchers and set up mechanisms for allocating and accessing these resources. In the context of cooperation with other academic institutions in the Lake Geneva region, it plans to pool certain resources, further develop the storage capacities and computational performance of existing IT installations and draw up charters governing their use.
4.2 Assist researchers in the use of scientific computing
In order to take full advantage of existing state-of-the-art IT infrastructure, researchers and those working to install this infrastructure need to be supported by people who are experts in scientific computing. The University plans to develop a platform that will support researchers in the use of high performance computing and supercomputing software, the implementation of new computational methods and algorithms, as well as data visualization techniques.
4.3 Create a data science competence center
The 21st century can in many ways be considered the data century. The ability to extract value from massive complex data sets will gradually become part of the toolbox of a growing number of scientific disciplines. With this in mind, the Rectorate has launched the creation of a Data Science Competence Center whose mission is to pool UNIGE’s competences and initiatives in data science, with the aim, through cross-disciplinarity, of encouraging the emergence of innovative research and supporting a critical and informed transformation of scientific culture in the age of massive, incomplete and heterogeneous data.
4.4 Provide a service for scientific data management
Academic research is increasingly based on digital tools and technologies, leading to growing data production and new requirements for data preservation and sharing. Various services have been set up within the University to support researchers facing these developments, such as the digital services catalog, workshops on data management plans (DMP) and a website for research data. The University aims to provide researchers with extensive and coordinated support for data storage, data stewardship, sharing, support and funding mechanisms, as well as legal aspects.
4.5 Implement a roadmap for open science
In line with the open science movement and in order to respond to the requirements of funders for Open Access and research data management, the Rectorate decided to set up a steering committee to establish a roadmap for the implementation of actions in the areas of scientific publication, research data, training and awareness, research evaluation, and research integrity. The publication of the roadmap is scheduled for autumn 2020, and the concretization and realization of the objectives and initiatives selected will be the responsibility of the various bodies concerned (rectorate, faculties, services, transversal networks)
5. An open ecosystem for digital innovation
Innovation requires an environment conducive to reflection, sharing of ideas and collaborative work. This space is being built thanks to the pooling of human and material resources from different sectors of the University, as well as exchanges of experience and expertise in multi-institutional partnerships. By appointing a Vice-Rector in charge of Digital Technology and Innovation, the University of Geneva intends to emphasize the particular importance it gives to innovation, in particular by developing an innovation ecosystem based on collaborations with strategic partners in the community.
Activities and projects
5.1 Partner on digital technology with the Canton of Geneva and the University of Applied Sciences and Arts of Western Switzerland - Geneva
Faced with the challenges of digitalization, the Canton of Geneva, the University of Geneva and the University of Applied Sciences and Arts of Western Switzerland – Geneva (HES-SO Genève) have established a framework agreement to enhance collaboration. The purpose is to facilitate and encourage cooperation in the areas of education, continuing education, applied research and service delivery related to digital transformation. This collaboration will lead to joint activities around digital innovation, leveraging the skills of the three institutions by involving both students and academic researchers from UNIGE and HES-SO Genève as well as the Canton’s administrative staff. The agreement specifies the provision of internships, the organization of joint digital events, collaboration with students on diploma work and collaboration in cantonal, national and international research projects. The three institutions started working together within the framework of the 2019 Digital Day. In 2020, the State of Geneva entrusted the Digital Law Center with a legal expertise mandate in the field of cyber-insurance.
6. An agile and participative governance
As digital technology has implications for all activities carried out within the University, it is essential to establish adequate governance of the institution’s digital transformation, taking into account the various components of the University. This governance should allow the institution to remain informed about relevant digital activities and projects carried out throughout the University and elsewhere. Above all, the governance should enable the institution to innovate and develop new knowledge by bringing together key actors of the institution and fostering collaboration with external partners.
Activities and projects
6.1 Ensure a clear governance for the digital transformation of the University
In 2016, the Rectorate created a Digital Strategy Office (BSN) whose mission is to monitor and coordinate internal and external digital activities and projects and to develop a Digital Strategy for the entire institution. With the publication of this strategy, the Office’s tasks have changed significantly and have now evolved towards steering the implementation of the action plan. On this occasion, the Digital Strategy Office became the Digital Transformation Office (DTO). In its work, the DTO aims to use collaborative and cross-disciplinary work methods and formats, such as hackathons, idea laboratories or Digital Clinics designed to encourage the active involvement of members of the university community, through the creation of agile co-construction spaces, conducive to the exploration of innovative solutions.


