« Back to all publications
Download this list in a RIS file or a BIB file or a PDF file
|
 |
|||||||
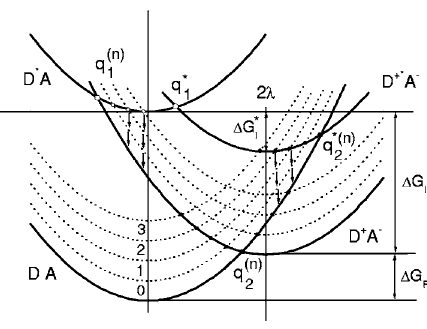
The recombination dynamics of ion pairs generated upon electron transfer quenching of perylene in the first singlet excited state by tetracyanoethylene in acetonitrile is quantitatively described by the extended unified theory of photoionization/recombination. The extension incorporates the hot recombination of the ion pair passing through the level-crossing point during its diffusive motion along the reaction coordinate down to the equilibrium state. The ultrafast hot recombination vastly reduces the yield of equilibrated ion pairs subjected to subsequent thermal charge recombination and separation into free ions. The relatively successful fit of the theory to the experimentally measured kinetics of ion accumulation/recombination and free ion yield represents a firm justification of hot recombination of about 90% of primary generated ion pairs. | ||||||||
|
||||||||
The synthesis, structural characterization, and photophysical behavior of a 14-membered tetraazamacrocycle with pendant 4-dimethylaminobenzyl (DMAB) and 9-anthracenylmethyl groups is reported (L3, 6-((9-anthracenylmethyl)amino)-trans-6,13-dimethyl-13-((4-dimethylaminobenzyl)amino)-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane). In its free base form, this compound displays rapid intramolecular photoinduced electron transfer (PET) quenching of the anthracene emission, with both the secondary amines and the DMAB group capable of acting as electron donors. When complexed with Zn(II), the characteristic fluorescence of the anthracene chromophore is restored as the former of these pathways is deactivated by coordination. Importantly, it is shown that the DMAB group, which remains uncoordinated and PET active, acts only very weakly to quench emission, by comparison to the behavior of a model Zn complex lacking the pendant DMAB group, [ZnL2]2+ (Chart 1). By contrast, Stern−Volmer analysis of intermolecular quenching of [ZnL2]2+ by N,N-dimethylaniline (DMA) has shown that this reaction is diffusion limited. Hence, the pivotal role of the bridge in influencing intramolecular PET is highlighted. | ||||||||
|
||||||||
The effect of the excitation wavelength on the charge recombination (CR) dynamics of several donor−acceptor complexes (DACs) composed of benzene derivatives as donors and of tetracyanoethylene or pyromellitic dianhydride as acceptors has been investigated in polar solvents using ultrafast time-resolved spectroscopy. Three different wavelength effects have been observed. (1) With complexes exhibiting two well-separated charge-transfer bands, the CR dynamics was found to be slower by a factor of about 1.5 upon excitation in the high-energy band. This effect was measured in both fast and slow relaxing solvents and was discussed in terms of different DAC geometries. (2) When the CR is faster than diffusive solvation, a slowing down of the CR with increasing excitation wavelength accompanied by an increase of the nonexponential character of the dynamics was measured. This effect appears only when exciting on the red edge of the charge-transfer absorption band. (3) When the driving force for CR is small, both nonequilibrium (hot) and thermally activated CR pathways can be operative. The results obtained with such a complex indicate that the relative contribution of these two paths depends on the excitation wavelength. | ||||||||
|
||||||||
Visible pump−probe spectroscopy has been used to identify and characterize short-lived metal-to-metal charge transfer (MMCT) excited states in a group of cyano-bridged mixed-valence complexes of the formula [LCoIIINCMII(CN)5]-, where L is a pentadentate macrocyclic pentaamine (L14) or triamine-dithiaether (L14S) and M is Fe or Ru. Nanosecond pump−probe spectroscopy on frozen solutions of [L14CoIIINCFeII(CN)5]- and [L14SCoIIINCFeII(CN)5]- at 11 K enabled the construction of difference transient absorption spectra that featured a rise in absorbance in the region of 350−400 nm consistent with the generation of the ferricyanide chromophore of the photoexcited complex. The MMCT excited state of the Ru analogue [L14CoIIINCRuII(CN)5]- was too short-lived to allow its detection. Femtosecond pump−probe spectroscopy on aqueous solutions of [L14CoIIINCFeII(CN)5]- and [L14SCoIIINCFeII(CN)5]- at room temperature enabled the lifetimes of their CoII−FeIII MMCT excited states to be determined as 0.8 and 1.3 ps, respectively. | ||||||||
|
||||||||
The emission from two photoactive 14-membered macrocyclic ligands, 6-((naphthalen-1-ylmethyl)-amino)-trans-6,13-dimethyl-13-amino-1,4,8,11-tetraaza-cyclotetradecane (L1) and 6-((anthracen-9-ylmethyl)-amino)-trans-6,13-dimethyl-13-amino-1,4,8,11-tetraaza-cyclotetradecane (L2) is strongly quenched by a photoinduced electron transfer (PET) mechanism involving amine lone pairs as electron donors. Time-correlated single photon counting (TCSPC), multiplex transient grating (TG), and fluorescence upconversion (FU) measurements were performed to characterize this quenching mechanism. Upon complexation with the redox inactive metal ion, Zn(II), the emission of the ligands is dramatically altered, with a significant increase in the fluorescence quantum yields due to coordination-induced deactivation of the macrocyclic amine lone pair electron donors. For [ZnL2]2+, the substituted exocyclic amine nitrogen, which is not coordinated to the metal ion, does not quench the fluorescence due to an inductive effect of the proximal divalent metal ion that raises the ionization potential. However, for [ZnL1]2+, the naphthalene chromophore is a sufficiently strong excited-state oxidant for PET quenching to occur. | ||||||||
 |
|
|||||||
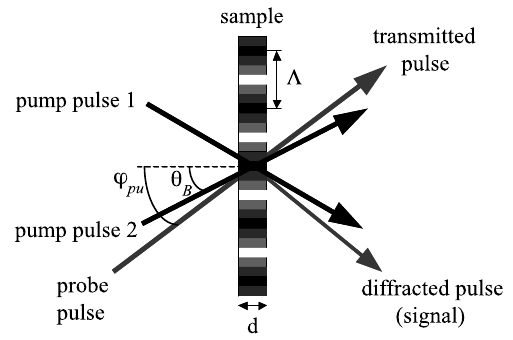
A new four-wave-mixing technique with evanescent optical fields generated by total internal reflection at a liquid-liquid interface is described. Several applications of this method to measure thermoacoustic and dynamic properties near liquid-liquid interfaces are presented. | ||||||||
|
 |
|||||||
Transient grating experiments performed with evanescent fields resulting from total internal reflection at an interface between a polar absorbing solution and an apolar transparent solvent are described. The time evolution of the diffracted intensity was monitored from picosecond to millisecond time scales. The diffracted signal originates essentially from two density phase gratings:Â one in the absorbing phase induced by thermal expansion and one in the transparent solvent due to electrostriction. A few nanoseconds after excitation, the latter grating is replaced by a thermal grating due to thermal diffusion from the absorbing phase. The speed of sound and the acoustic attenuation measured near the interface are found to be essentially the same as in the bulk solutions. However, after addition of a surfactant in the polar phase, the speed of sound near the interface differs substantially from that in the bulk with the same surfactant concentration. This effect is interpreted in terms of adsorption at the liquid/liquid interface. Other phenomena, which are not observed in bulk experiments, such as acoustic echoes and a fast oscillation of the signal intensity, are also described. | ||||||||
 |
|
|||||||
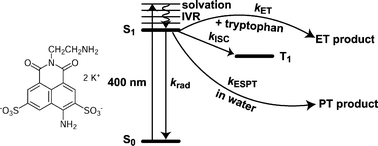
The photophysics of the dye Lucifer Yellow ethylenediamine (LYen) has been investigated in various polar solvents. The main deactivation pathways of its first singlet excited state are the fluorescence and the intersystem crossing. In water, non-radiative decay by intermolecular proton transfer becomes a significant deactivation channel. The early fluorescence dynamics, which was investigated in liquids and in reverse micelles, was found to depend substantially on the environment. An important static quenching of LYen by tryptophan and indole occurring in the subpicosecond timescale was observed. The use of the fluorescence dynamics of LYen as a local probe is illustrated by preliminary results obtained with a biotinylated Lucifer Yellow derivative complexed with avidin. | ||||||||
|
Download this list in a RIS file or a BIB file or a PDF file
Contact:
Eric Vauthey
Physical Chemistry Department - Sciences II - University of Geneva
30, Quai Ernest Ansermet - CH-1211 Geneva 4 (Switzerland)
© All rights reserved by Eric Vauthey and the University of Geneva
Design and code by Guillaume Duvanel