Interpreting emotions: a matter of confidence
UNIGE and HUG researchers have been measuring how much confidence we have in our interpretations of other people’s emotions, and how that confidence is skewed by our experiences.
© UNIGE
We are constantly exposed to the facial expressions of the people around us, expressions that reflect their emotions. But do we interpret them correctly? And do we trust our own judgment? This trust is essential for avoiding misunderstandings or even potentially dangerous situations. That is the reason why researchers from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) and University Hospitals of Geneva (HUG), Switzerland, have been testing how confident we feel when judging other people’s emotions, and what areas of the brain are used. These results – which you can read all about in the journal Social, Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience – demonstrate that beliefs of our own emotional interpretation stem directly from the experiences stored in our memory. In other words, our past life influences our interpretations… and sometimes leads us astray.
Our daily decisions come with a degree of confidence, yet confidence doesn’t always go hand in hand with decision’s accuracy. We are sometimes wrong even when we are entirely confident in having taken the right decision – as, for instance, when making a poor investment on the stock market. The same goes for our social interactions: we are constantly interpreting the expressions on the faces of those around us, and the belief we have in our own interpretations is paramount. “Take the case of Trayvon Martin in the US, which is a perfect illustration of this,” suggests Indrit Bègue, a post-doctoral researcher in the Department of Psychiatry in UNIGE’s Faculty of Medicine and a doctor in the Adult Psychiatry Service in the Department of Psychiatry and Mental Health at HUG. “Trayvon was a 17-year-old African-American teenager who was shot dead by George Zimmerman, despite being unarmed. Zimmerman thought the young boy “looked suspicious”, an altercation broke out with the fatal outcome that we’re all familiar with.” But why was Zimmerman so sure that Martin “looked suspicious” and thus, was dangerous, when all he was actually doing was waiting in front of his father’s house? It is in an attempt to answer this type of question that the UNIGE and HUG researchers were so keen to test the level of confidence we have in our interpretations of the emotional behaviour of others, and to discover which areas of the brain are activated during these interpretations.
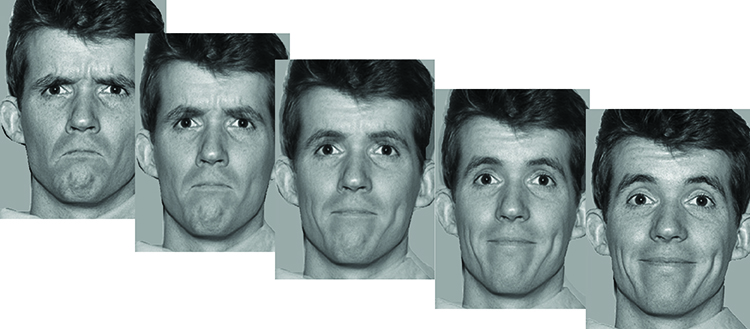
Emotion recognition: overconfidently wrong
The scientists decided to measure confidence-related behaviour by asking 34 participants to judge emotional faces displaying a mix of happy and angry emotions, with each face being framed by two horizontal bars of varying thickness. Some of the faces were very clearly happy or angry, while others were highly ambiguous. The participants first had to define what emotion was represented on each of the 128 faces that flashed up. They, then, had to choose which of the two bars was thicker. Finally, for every decision they made, participants had to indicate their level of confidence in their choice on a scale ranging from 1 (not at all sure) to 6 (certain). “The bars were used to evaluate their confidence in visual perception, which has already been studied in depth. Here it served as a control mechanism,” says Patrik Vuilleumier, a professor in UNIGE’s Department of fundamental neurosciences.
The results of the tests surprised the researchers, to say the least. “Strikingly, the average level of confidence in emotional recognition was higher (5.88 points) than for visual perception (4.95 points), even though participants made more errors in emotional recognition (79 % correct answers) than with the lines (82% correct answers)!” says Indrit.
In fact, learning emotional recognition is not as easy as for perception: our interlocutors may be ironic, lying or prevented from expressing their facial emotions due to social conventions – if their boss is present, for instance. It follows that it is more difficult to correctly calibrate our confidence in recognising other people’s emotions in the absence of any feedback. In addition, we have to interpret an expression very quickly because it is fleeting. So, we feel that our first impression is the right one, and trust our judgment about an angry face or mouth. On the other hand, judging perception may be more attentive and benefits from direct feedback about its accuracy. If there is hesitation, confidence is lower than for emotions, because we know that we can easily be wrong and be contradicted.
Confidence based on memory
As for the brain correlates, the UNIGE and HUG researchers examined the neural mechanisms during this process of confidence on one’s emotional recognition by providing participants with a functional MRI. “When the participants judged the lines, the perception (visual areas) and attention (frontal areas) zones were activated. But when assessing confidence in recognising emotions, areas linked to autobiographical and contextual memory lit up, such as the parahippocampal gyrus and the retrosplenial/posterior cingulate cortex,” points out professor Vuilleumier. This demonstrates that brain systems storing personal and contextual memories are directly involved in beliefs on emotional recognition, and that they determine the accuracy of the interpretation of facial expressions and the trust placed in them. “The fact that past experiences are so fundamental to govern our confidence may cause problems in our day-to-day life, because they can skew our judgment, as happened in the Trayvon Martin case, when Zimmerman didn’t see just an impatient young man waiting outside his home, but an angry black man lurking in front of a house,” explains Indrit. “That’s why it’s crucial to give feedback about our emotions early on, so we can teach children to interpret them correctly.”
