Article on Protein affinity for TiO2 and CeO2 manufactured nanoparticles. From ultra-pure water to biological media published in Colloids and Surfaces A
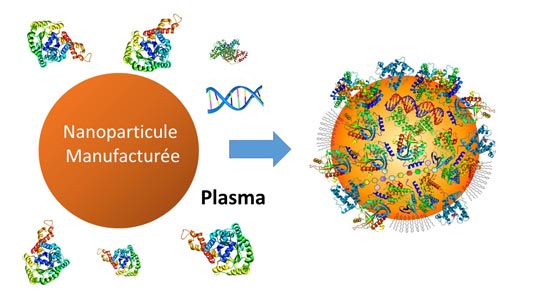
This study aims to clarify the behavior of manufactured nanoparticles in biological media. Transport, transformation and interaction of nanoparticles in plasma are of high importance for the evaluation of nanoparticle risk assessment regarding human health. Such aspects are difficult to study owing to the complexity of biological fluids and nanoparticle properties. Our findings indicate that, in all cases, initially dispersed TiO2 or CeO2 NPs are stabilized by the presence of proteins and that protein adsorption is fast regarding nanoparticle homoaggregation. Proteins are found to improve nanoparticle dispersion even at high ionic strength with overarching consequences on the fate, transport and related risk of nanoparticles in living systems.
Huber, R., et Stoll, S., 2018, Protein affinity for TiO2 and CeO2 manufactured nanoparticles. From ultra-pure water to biological media: Colloids and Surfaces. A, Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, v. 553, p. 425-431.
30 Jul 2018
