Towards a better control of glycemia in type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes affects millions of people worldwide, and its incidence continues to rise globally. Despite significant advances in medical science, the management of type 1 diabetes remains a major challenge, with current treatment modalities failing to achieve optimal blood glucose control while minimizing complications.
A co-treatment with fewer side effects…
In their recent publication in Science Advances, researchers from the laboratory of Prof. Roberto Coppari have unveiled a new insulin independent strategy that shows remarkable promise for reducing insulin needs and improving glycemic control, thus limiting the drawbacks associated with traditional insulin therapy.
This innovative approach, which involves co-treatment with the recombinant S100 calcium-binding protein A9 (S100A9), has been shown in mice to normalize glycemia with significantly reduced insulin doses. The co-administration of S100A9 is even able to limit the life-threatening complications that can occur when using insulin alone. These include ketoacidosis, the sudden increase in ketones and acidification of the blood (in yellow in the Figure below) and hypoglycemia (in red in the Figure below).
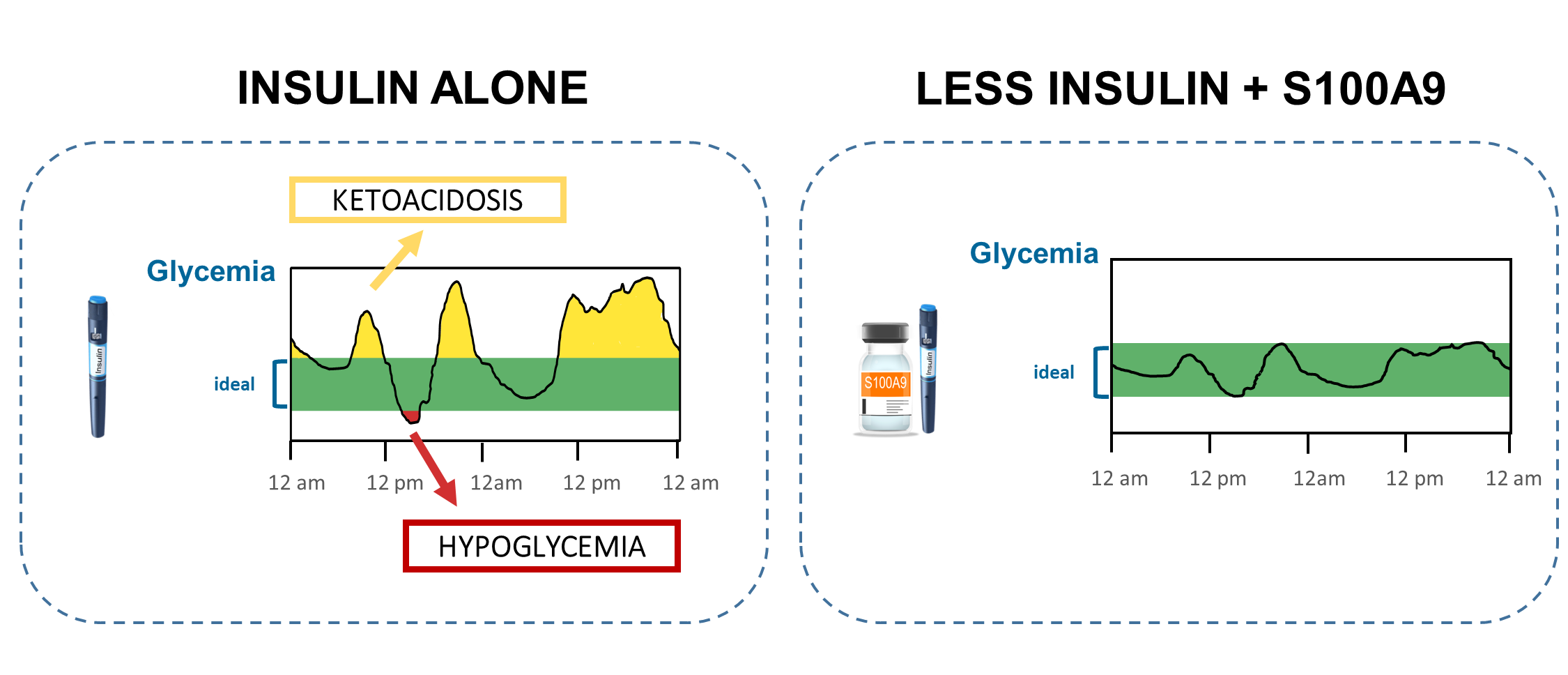
Co-treatment with the recombinant S100 calcium-binding protein A9 (S100A9) has been shown to normalize glycemia and limit life-threatening ketoacidosis and hypoglycemia events (right panel) which often occur with insulin alone (left panel) © Laboratory of Prof. Roberto Coppari UNIGE
… and an additional anti-inflammatory effect
The study also revealed that diabetic mice treated with S100A9 alone, or in combination with less insulin, experienced a resolution of abnormal systemic inflammation, highlighting an additional anti-inflammatory benefit of this therapy.
With further research and clinical trials, this discovery has the potential to revolutionize the management of type 1 diabetes, offering new hope to millions of people living with this challenging condition.
