Analysis of proteins expression and solubility
Protein synthesis is a final outcome of efficient translation. Proteins folding occurs during translation (co-translationally) or after translation (post-translationally) and requires help of the chaperones and other assisting factors. Not correctly folded proteins become insoluble forming aggregates. The ribosome itself is emerging as a central actor in protein folding and quality control processes, acting as a proofreader during protein biogenesis and initiating downstream events that regulate the fate of nascent chains. Speed of translation may impact correct folding of newly synthesized peptides.
R2P Core Facility provides isolation of soluble and insoluble proteins which is based on fractionation of cellular components with different size and solubility in detergents.
Profile of total protein solubility allows visualize general outcome of translation in the cell (fig. 1) or translational outcome of the particular protein of interest (fig. 2).
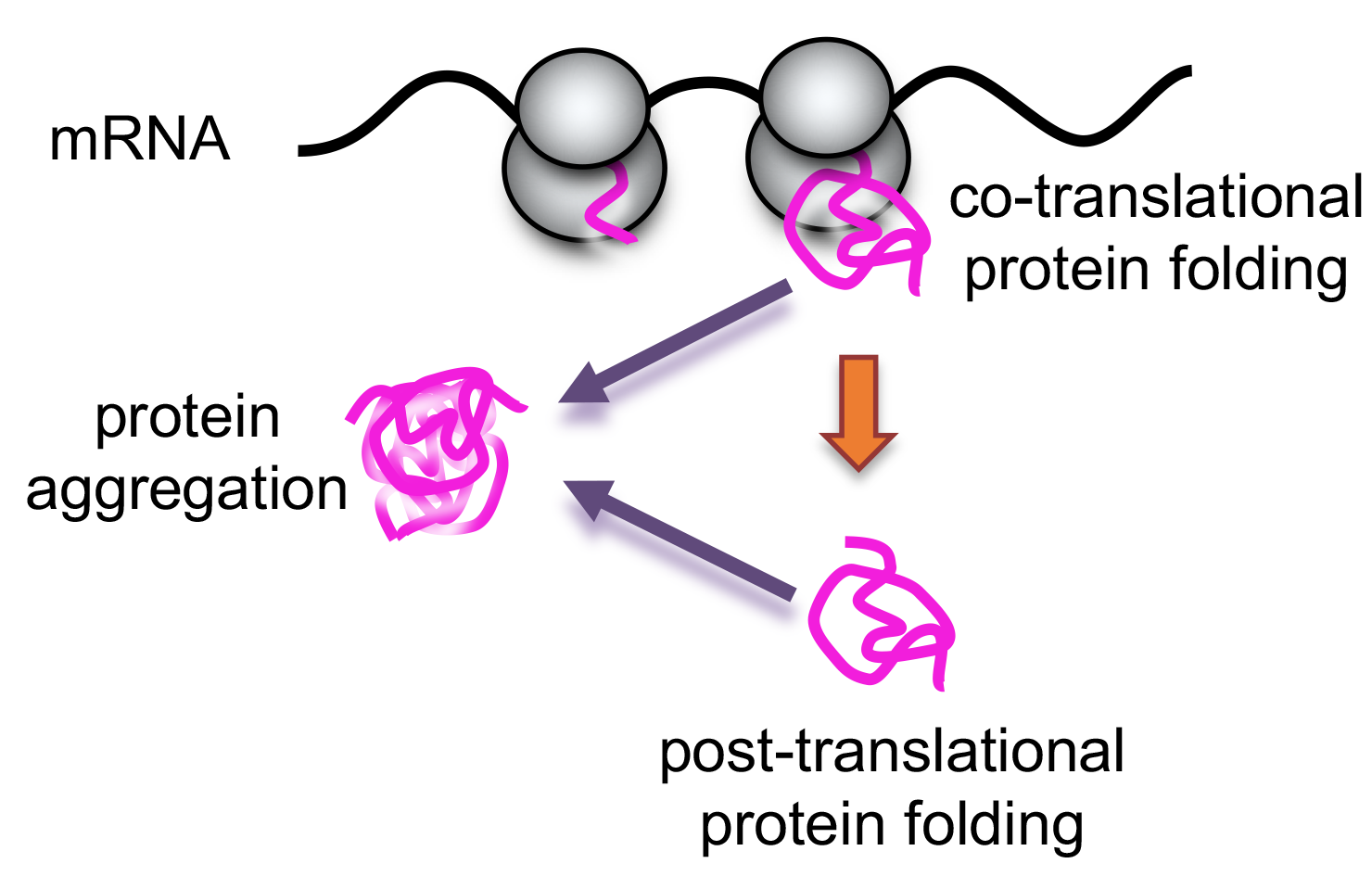
Fig. 1. Staphylococcus aureus proteome aggregates upon stress and antibiotic treatment (1)
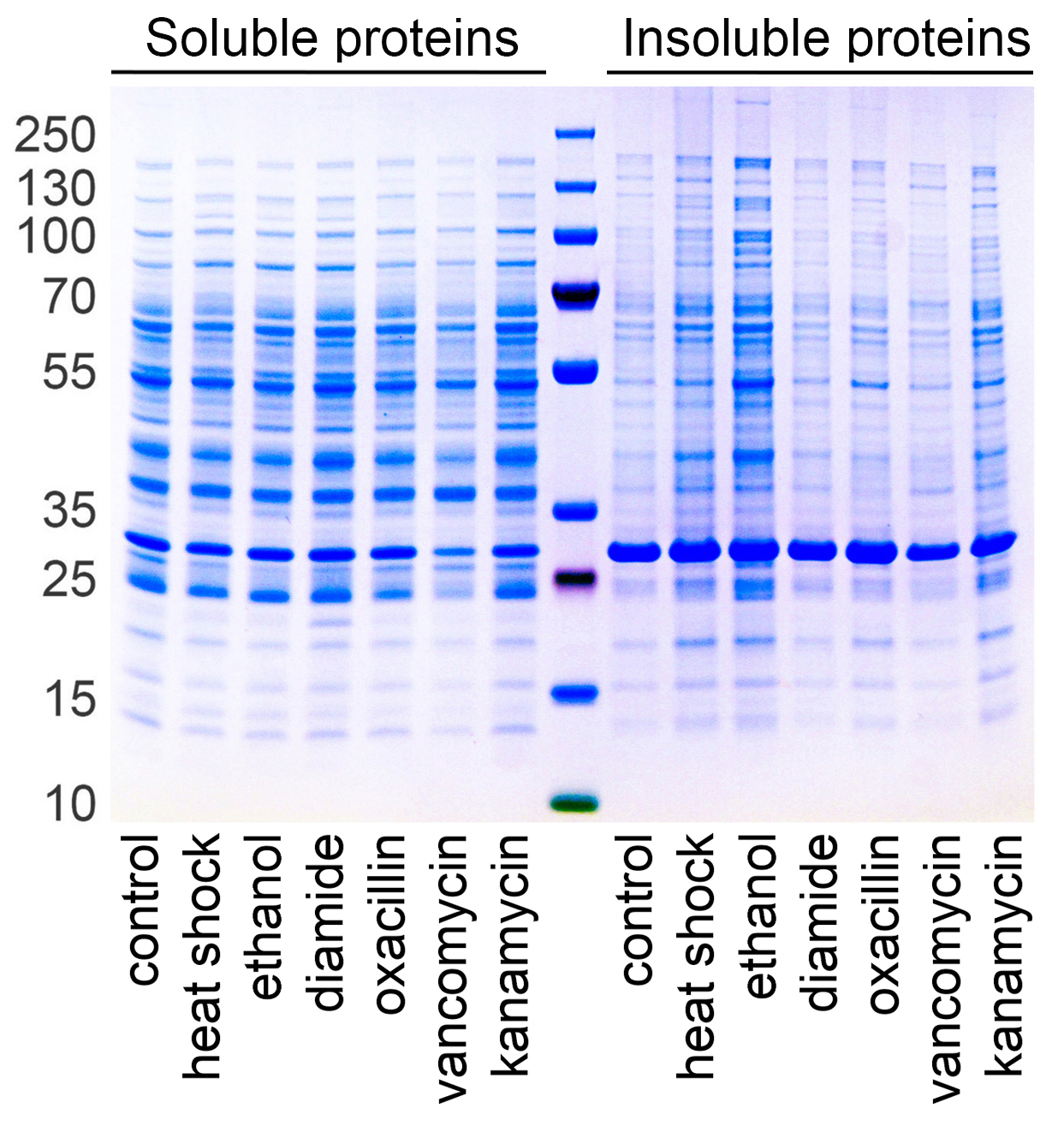
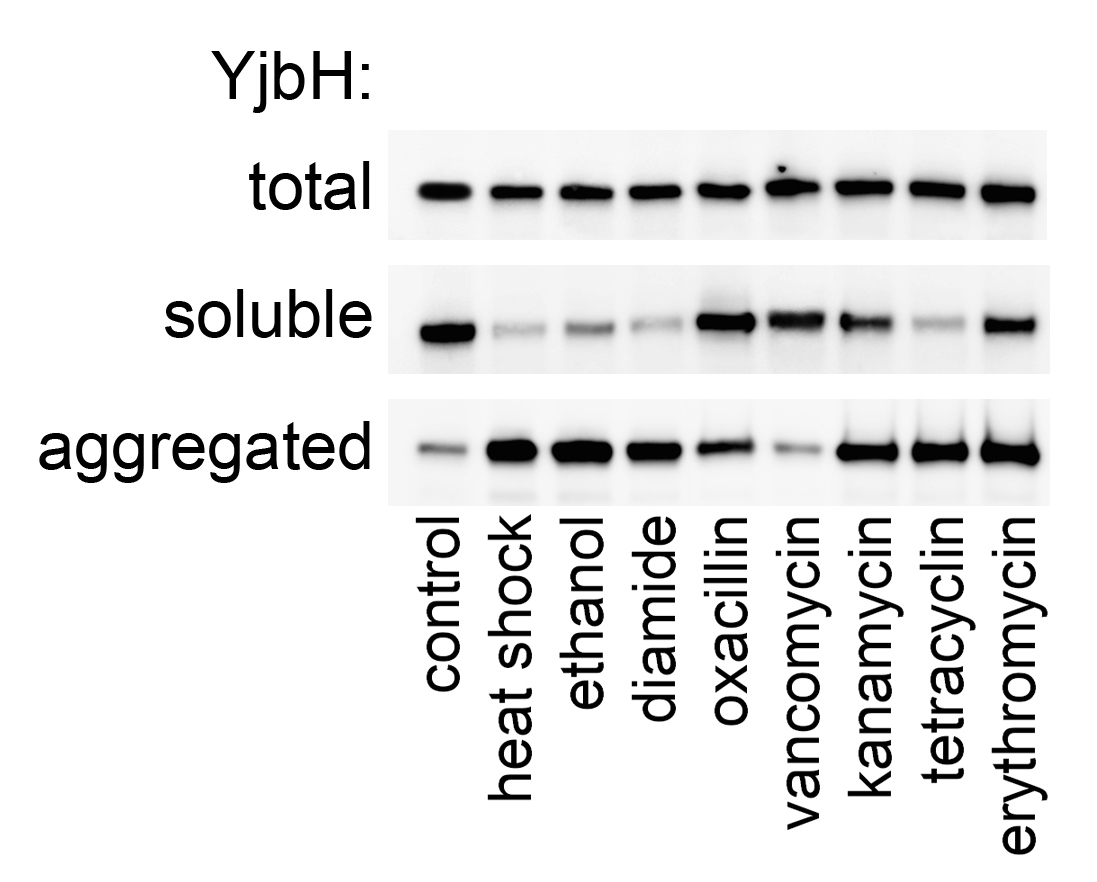
Fig. 2. YjbH is an adaptor protein required for targeted degradation in S. aureus. YjbH is aggregated upon heat shock, oxidative stress and antibiotics (1)
1. O. Panasenko, F. Bezrukov, O. Komarynets, A. Renzoni (2020), YjbH Solubility Controls Spx in Staphylococcus aureus: Implication for MazEF Toxin-Antitoxin System Regulation. Frontiers in Microbiology, 11, 113
